[React.js] 리액트 라이프 사이클(React Lifecycle)

포스팅 계기
당연한 말일 수도 있지만, 안드로이드, 웹 프레임워크 등 모두 life cycle을 잘 이해해야 탄탄한 개발을 할 수 있다. 이제 리액트를 시작하는 단계이기 때문에, life cycle부터 공부해보기로 했다. 라이프 사이클을 이해하기 위해서 React 인스턴스 property(props와 state) 개념이 선행될 필요가 있다. 아직 두 개념에 대한 이해가 부족하다면 위의 링크를 통해 공부하길 추천한다.
Life cycle (ver 16.4^)
기존 Life cycle과는 다소 차이가 있다. 하지만 React blog에서 밝히는 변경이유는 아래와 같다.
- 초기 렌더링 작업을 제어하는 방법이 너무 많아서 혼란이 됨.
- Error Handling의 중단 작업이 고려되지 않아서 memory leak을 야기할 수 있음.
- React 커뮤니티에서도 혼란이 됨 (...?리린이라 잘 공감하지 못함)
이제는 현재 사용중인 Life cycle을 다이어그램을 통해 top-down 방식으로 보도록 해보자.
주황색 lifecycle은 잘 사용하지 않는다.
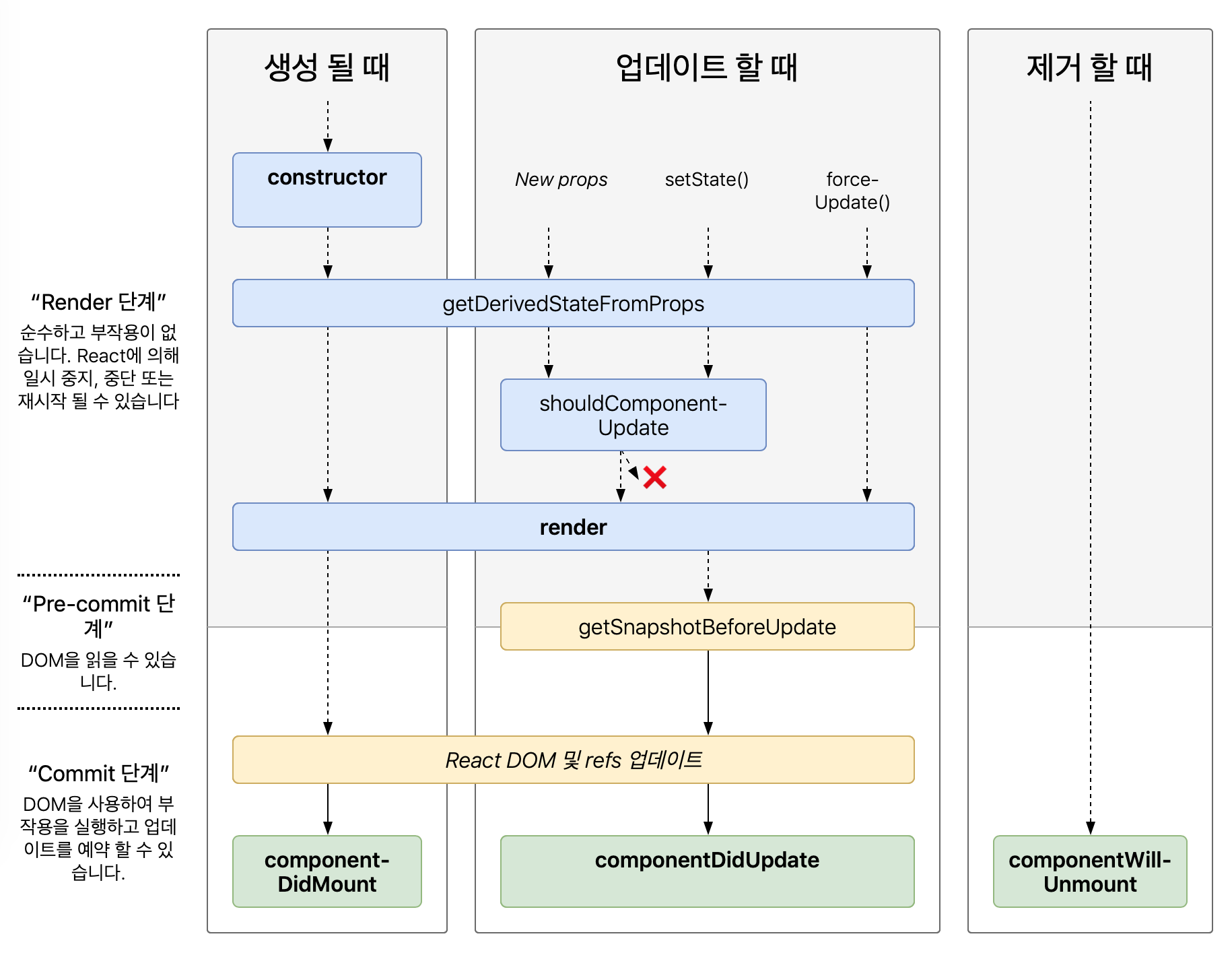
마운트
아래 메서드들은 컴포넌트의 인스턴스가 생성되어 DOM 상에 삽입될 때에 순서대로 호출된다.
- constructor()
- this.state에 객체를 할당하여 local state를 초기화
- 인스턴스에 이벤트 처리 메서드(onClick...)를 바인딩
constructor(props) {
super(props); // 선언해주지 않으면 버그로 이어질 수 있음.
this.state = { counter: 0 }; // state 정의
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this); // 이벤트 처리 메서드 바인딩
}- getDerivedStateFromProps()
- props에 의해 state를 갱신하기 위한 객체 반환
- 권장) props의 변화에 따른 이벤트가 필요하다면, componentDidUpdate()
- 권장) props의 변화에 따른 데이터 계산이 필요하다면, Memoziation Helper
- 권장) props의 변화에 따른 일부 state 값의 재설정이 필요하다면, 완전 제어 컴포넌트 또는 key를 사용하는 완전 비제어 컴포넌트
- render()
- 예상되는 output: React 엘리먼트, 배열과 Fragement(여러 엘리먼트), Protal(DOM 하위 트리에 자식 엘리먼트 렌더링), 문자열 &. 숫자(DOM 상의 텍스트 노드), Boolean || null (아무것도 렌더링 하지 않는다)
- 순수함수여야 한다. (호출될 때마다 동일한 output, state 변경 x)
- 권장) 브라우저와 상호작용하는 작업이 필요하다면, componentDidMount()
** shouldComponentUpate()가 false일시 render()는 호출되지 않는다.
- componentDidMount()
- 컴포넌트가 마운트된 직후, 즉 트리에 삽입된 직후 호출 됨.
- DOM 노드가 있어야하는 초기화 작업을 함.
- 비권장) setState() -> render()를 두번 호출하게 되므로 퍼포먼스 문제를 야기할 수 있음. -> constructor() 사용
** Depreated: componentWillMount()
업데이트
props 또는 state가 변경되면 갱신이 발생한다. 아래 메서드들은 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링될 때 순서대로 호출된다.
- getDerivedStateFromProps()
- shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
- props 또는 state가 새로운 값으로 갱신되어서 렌더링이 발생하기 직전 호출. (default: true)
- (nextProps, nextState), (this.props, this.state)의 비교를 통해 성능 최적화를 위해 사용할 수 있지만, JSON.stringify()를 통한 로직은 권장하지 않음. -> 성능 비효율
- 권장) pureComponent로 사용
- render()
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
- 가장 마지막으로 렌더링된 결과가 DOM 등에 반영되었을 때 호출 됨.
- 컴포넌트가 DOM으로부터 스크롤 위치와 같은 정보를 변경되기 전에 사용할 수 있음
- ouput은 componentDidUpdate()에 전달 됨.
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
// Are we adding new items to the list?
// Capture the scroll position so we can adjust scroll later.
if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;
}
return null;
}
- componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
- 갱신이 일어난 직후에 호출 됨.
- 컴포넌트가 갱신되었을 때 DOM을 조작하기 위해 활용 (i.e props를 비교하여 네트워크 요청)
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate의 snapshot이 있을 때 핸들링
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
// 전형적인 사용 사례 (props 비교를 잊지 마세요)
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
// getSnapshotBeforeUpdate로부터의 snapshot이 있을 때 사용
// 새로운 list item이 추가되면 scroll 위치를 변경함
if (snapshot !== null) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;
}
}컴포넌트가 갱신되었을 때 DOM을 조작하기 위하여 이 메서드를 활용
** Depreated: componentWillUpdate(), componentWillReceiveProps()
마운트 해제
아래 메서드는 컴포넌트가 DOM 상에서 제거될 때에 호출된다.
- componentWillUnmount()
- 컴포넌트가 마운트 해제되어 제거되기 직전에 호출 됨.
- 타이머 제거, 네트워크 요청 취소 등 componentDidMount()에서 생성된 것들을 해제
- 주의) 다시 렌더링되지 않으므로 setState()를 호출하면 안됨
에러
아래 메서드들은 자식 컴포넌트를 렌더링하거나, 자식 컴포넌트가 생명주기 메서드를 호출하거나, 또는 자식 컴포넌트가 생성자 메서드를 호출하는 과정에서 오류가 발생했을 때에 호출된다.
- getDerivedStateFromError(error)
- Child 컴포넌트에서 오류가 발생했을 때 호출 됨.
- 매개변수로 오류를 전달받고, 갱신된 state 값을 반환해야 함.
- render 단계에서 호출되므로 side-effect를 사용하면 안됨. -> componentDidCatch()에서 사용
- error를 통한 대체된 UI를 렌더링.
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// state를 갱신하여 다음 렌더링에서 대체 UI를 표시합니다.
return { hasError: true };
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// 별도로 작성한 대체 UI를 렌더링할 수도 있습니다.
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}- componentDidCatch(error, info)
- Child 컴포넌트에서 오류가 발생했을 때 호출 됨.
- info -> 어떤 컴포넌트가 오류를 발생시켰는지에 대한 정보(componentStack 키를 가진 객체)
- commit 단계에서 호출되므로 오류 로그 기록 등을 위해 사용 함.
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// state를 갱신하여 다음 렌더링에서 대체 UI를 표시합니다.
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
// Example "componentStack":
// in ComponentThatThrows (created by App)
// in ErrorBoundary (created by App)
// in div (created by App)
// in App
logComponentStackToMyService(info.componentStack);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// 별도로 작성한 대체 UI를 렌더링할 수도 있습니다.
return <h1>Something went wrong.</h1>;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
참고
https://velopert.com/1130
https://www.zerocho.com/category/React/post/579b5ec26958781500ed9955
https://velog.io/@kyusung/리액트-교과서-컴포넌트와-라이프사이클-이벤트
https://ko.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html